Glassy aerosol particles
Formation of glassy aerosols in the atmosphere
In a study (Zobrist et al. ACP 2008) we investigated the glass temperatures of different concentrated organic, inorganic and organic/inorganic aqueous solutions using a Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC). The atmospheric influence of glassy aerosols is intensely discussed in that manuscript, with implication for:
- Water uptake of aerosols
- Chemical reactions, e.g. Ozonolysis
- Crystal growth, e.g. Ice
- Ice nucleation in super cooled liquid aerosols
Background
Glasses are amorphous substances that behave mechanically like solids. The ability to form a glass depends strongly on the chemical and physical properties of a given substance and its mixing state. At the glass temperature, Tg the liquid reaches viscosities in the order of 1012 Pa s, and thus the molecular motion becomes so slow, that the sample vitrifies within timescales of seconds to minutes. During the glass transition neither a release of latent enthalpy, thus, it can not be considered as a first-order phase transition. The liquid-to-glass transformation denotes a change in the heat capacity of the sample, whereas the liquid phase exhibits the higher one.
Experimental investigation of the glass transition temperature, Tg, using a DSC
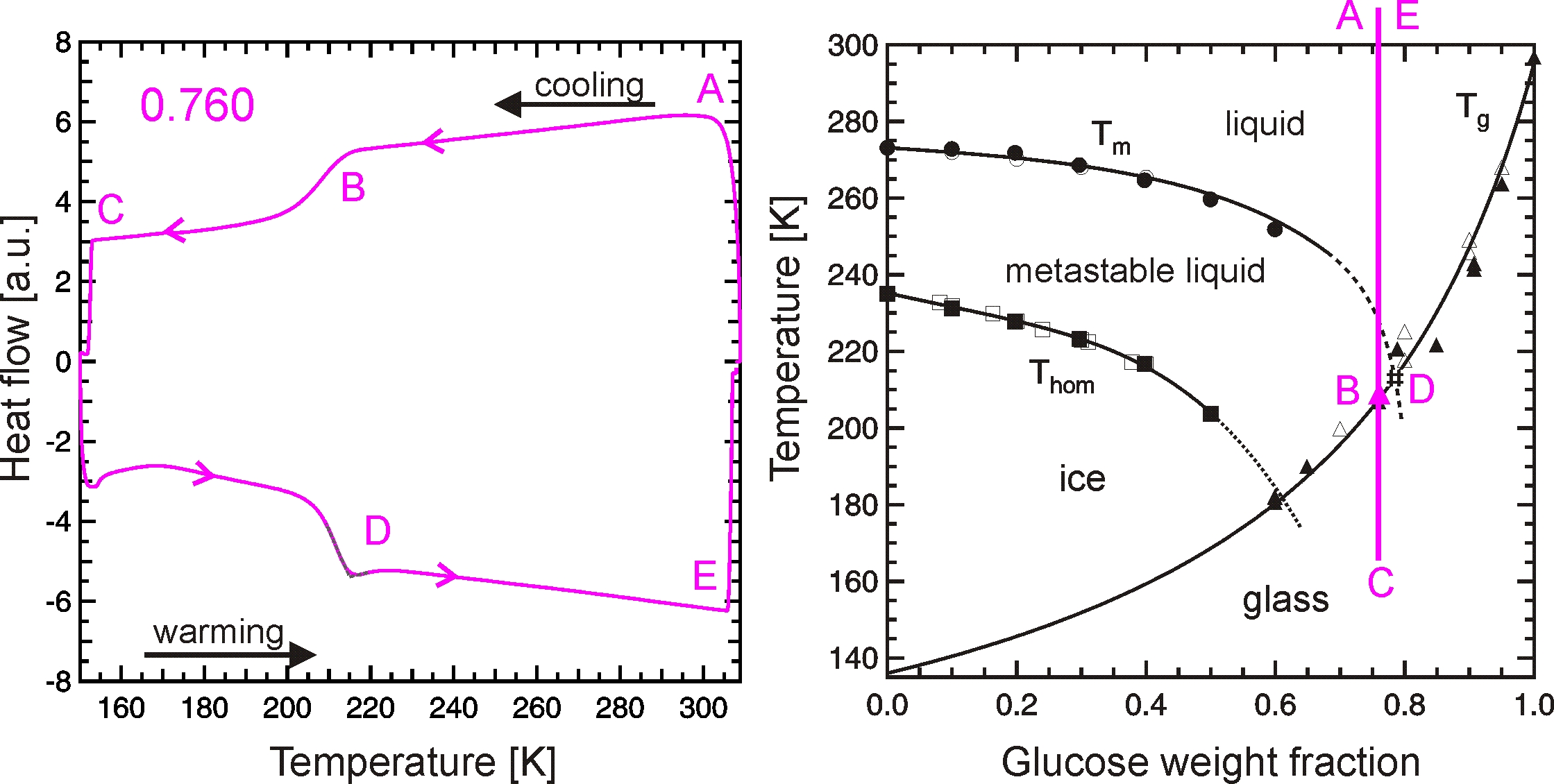
A DSC is very well suited for investigations of glass transition as well as for crystal growth. The figure below shows the DSC thermogram of an emulsified 76.0 wt% aqueous sucrose solution sample (left panel) and the pathway of this experiment in the sucrose/water state diagram (right panel). The smooth S-shaped step in the left panel at roughly 210 K (point B) is attributed to the glass transition, which is found in the state diagram (right panel) when the experimental pathway (magenta line) crosses the glass curve at point B.
Inorganic versus organic solutes
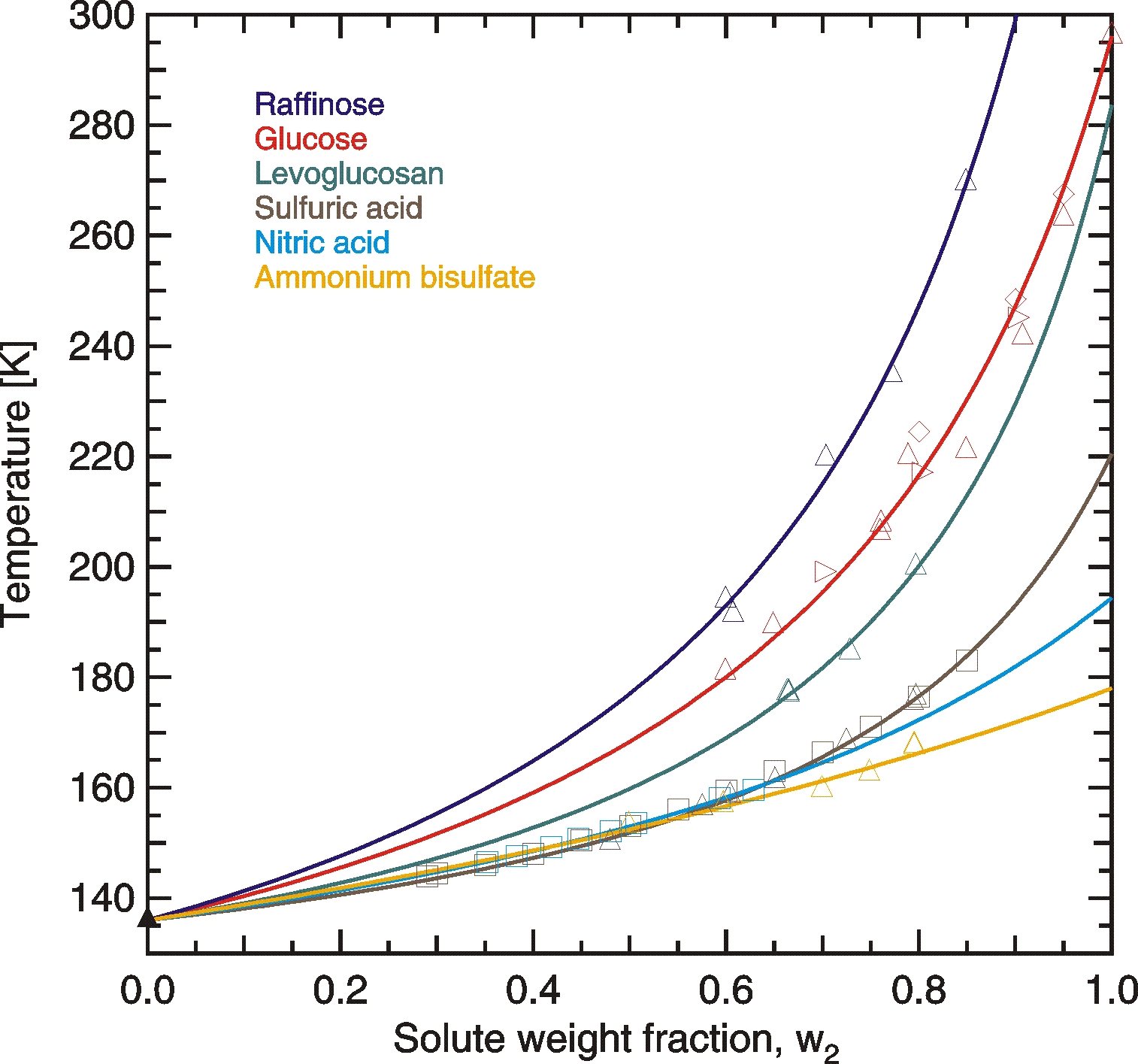
Aqueous inorganic solutions containing sulfuric acid, ammonium bisulfate or nitric acid form glasses at high solute concentrations, but Tg rarely exceed 180 K. Ammonium sulfate and ammonium nitrate solutions did not form glasses when using moderate cooling rates, because either ice or the solute precipitated beforehand. Therefore, we consider it unlikely that such inorganic solutions form glasses under atmospheric conditions.
Aqueous organic solutions undergo glass transitions typicallyat higher temperatures than inorganic solutions at similar concentrations. Tg of such solutions depend predominantly on the molar mass of the organic solute with a larger molar mass leading to a higher Tg.